 优化与源码
优化与源码
# 优化
# 扩展序列化算法
序列化,反序列化主要用在消息正文的转换上
- 序列化时,需要将 Java 对象变为要传输的数据(可以是 byte[],或 json 等,最终都需要变成 byte[])
- 反序列化时,需要将传入的正文数据还原成 Java 对象,便于处理
目前的代码仅支持 Java 自带的序列化,反序列化机制,核心代码如下
// 反序列化
byte[] body = new byte[bodyLength];
byteByf.readBytes(body);
ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(body));
Message message = (Message) in.readObject();
message.setSequenceId(sequenceId);
// 序列化
ByteArrayOutputStream out = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
new ObjectOutputStream(out).writeObject(message);
byte[] bytes = out.toByteArray();
为了支持更多序列化算法,抽象一个 Serializer 接口
public interface Serializer {
// 反序列化方法
<T> T deserialize(Class<T> clazz, byte[] bytes);
// 序列化方法
<T> byte[] serialize(T object);
}
提供两个实现
public enum SerializerAlgorithm implements Serializer{
/**
* Java 实现
*/
Java{
@Override
public <T> T deSerialize(Class<T> clazz, byte[] bytes) {
try {
ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes));
Object object = in.readObject();
return (T) object;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("反序列化失败", e);
}
}
@Override
public <T> byte[] serialize(T object) {
try {
ByteArrayOutputStream out = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
new ObjectOutputStream(out).writeObject(object);
return out.toByteArray();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("序列化失败", e);
}
}
},
/**
* Json 实现
*/
Json{
@Override
public <T> T deSerialize(Class<T> clazz, byte[] bytes) {
return JSONUtil.toBean(new String(bytes, StandardCharsets.UTF_8), clazz);
}
@Override
public <T> byte[] serialize(T object) {
return JSONUtil.toJsonStr(object).getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
}
}
}
增加配置类和配置文件
public abstract class Config {
static Properties properties;
static {
try (InputStream in = Config.class.getResourceAsStream("/application.properties")) {
properties = new Properties();
properties.load(in);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new ExceptionInInitializerError(e);
}
}
public static int getServerPort() {
String value = properties.getProperty("server.port");
if(value == null) {
return 8080;
} else {
return Integer.parseInt(value);
}
}
public static SerializerAlgorithm getSerializerAlgorithm() {
String value = properties.getProperty("serializer.algorithm");
if(value == null) {
return SerializerAlgorithm.Java;
} else {
return SerializerAlgorithm.valueOf(value);
}
}
}
配置文件
serializer.algorithm=Json
修改编解码器
@Slf4j
@ChannelHandler.Sharable
public class MessageCodecSharable extends MessageToMessageCodec<ByteBuf,Message> {
/**
* 魔数
*/
private static final byte[] MAGIC_NUMBER = new byte[]{1, 2, 3, 6};
/**
* 版本号
*/
private static final byte VERSION = 1;
@Override
protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Message msg, List<Object> out) throws Exception {
ByteBuf buf = ctx.alloc().buffer();
// 4 字节,自定义 魔数
buf.writeBytes(MAGIC_NUMBER);
// 1 字节,版本号
buf.writeByte(VERSION);
// 1 字节,序列化算法 0 JDK、1 JSON
buf.writeByte(Config.getSerializerAlgorithm().ordinal());
// 1 字节,指令类型
buf.writeByte(msg.getMessageType());
// 4 字节,请求序号
buf.writeInt(msg.getSequenceId());
// 1 字节,对齐填充,使固定长度为2的倍数
buf.writeByte(0xff);
byte[] bytes = Config.getSerializerAlgorithm().serialize(msg);
// 4 字节,正文长度
buf.writeInt(bytes.length);
// 消息正文
buf.writeBytes(bytes);
out.add(buf);
}
@Override
protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf msg, List<Object> out) throws Exception {
// 魔数判断
byte[] magicNumber = new byte[MAGIC_NUMBER.length];
msg.readBytes(magicNumber, 0, MAGIC_NUMBER.length);
if (!Arrays.equals(MAGIC_NUMBER, magicNumber)) {
throw new RuntimeException();
}
byte version = msg.readByte();
// 序列发方式
byte serializerType = msg.readByte();
// 消息类型
byte messageType = msg.readByte();
int sequenceId = msg.readInt();
msg.readByte();
int length = msg.readInt();
byte[] bytes = new byte[length];
msg.readBytes(bytes, 0, length);
// 具体序列化算法
SerializerAlgorithm serializerAlgorithm = SerializerAlgorithm.values()[serializerType];
// 获取消息类型
Class<? extends Message> messageClass = Message.getMessageClass(messageType);
Message message = serializerAlgorithm.deSerialize(messageClass, bytes);
log.info("{}|{}|{}|{}|{}|{}", magicNumber, version, serializerType, messageType, sequenceId, length);
log.info("{}", message);
// 放入 list 供下个 handler 处理
out.add(message);
}
}
测试
public class TestProtocol {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MessageCodecSharable codec = new MessageCodecSharable();
LoggingHandler loggingHandler = new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG);
EmbeddedChannel embeddedChannel = new EmbeddedChannel(loggingHandler, codec, loggingHandler);
LoginRequestMessage message = new LoginRequestMessage("zhangsan", "123");
//embeddedChannel.writeOutbound(message);
ByteBuf buf = messageToBytes(message);
embeddedChannel.writeInbound(buf);
}
static ByteBuf messageToBytes(Message msg) {
ByteBuf buf = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer();
buf.writeBytes(new byte[]{1,2,3,6});
buf.writeByte(1);
buf.writeByte(Config.getSerializerAlgorithm().ordinal());
buf.writeByte(msg.getMessageType());
buf.writeInt(msg.getSequenceId());
buf.writeByte(0xff);
byte[] bytes = Config.getSerializerAlgorithm().serialize(msg);
buf.writeInt(bytes.length);
buf.writeBytes(bytes);
return buf;
}
}
# 参数调优
性能调优主要有以下三大方向:
- Linux系统参数调整。
- TCP参数调整。
- Netty服务器应用层优化。
# CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MILLIS
- 属于
SocketChannal参数 - 用在客户端建立连接时,如果在指定毫秒内无法连接,会抛出 timeout 异常
SO_TIMEOUT主要用在阻塞 IO,阻塞 IO 中accept,read等都是无限等待的,如果不希望永远阻塞,使用它调整超时时间
@Slf4j
public class TestConnectionTimeout {
public static void main(String[] args) {
NioEventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap()
.group(group)
.option(ChannelOption.CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MILLIS, 300)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new LoggingHandler());
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.connect("127.0.0.1", 8080);
future.sync().channel().closeFuture().sync(); // 断点1
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
log.debug("timeout");
} finally {
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
另外源码部分io.netty.channel.nio.AbstractNioChannel.AbstractNioUnsafe#connect
@Override
public final void connect(
final SocketAddress remoteAddress, final SocketAddress localAddress, final ChannelPromise promise) {
// ...
// Schedule connect timeout.
int connectTimeoutMillis = config().getConnectTimeoutMillis();
if (connectTimeoutMillis > 0) {
connectTimeoutFuture = eventLoop().schedule(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
ChannelPromise connectPromise = AbstractNioChannel.this.connectPromise;
ConnectTimeoutException cause =
new ConnectTimeoutException("connection timed out: " + remoteAddress); // 断点2
if (connectPromise != null && connectPromise.tryFailure(cause)) {
close(voidPromise());
}
}
}, connectTimeoutMillis, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
// ...
}
连接时会有一个定时任务,指定时间(ChannelOption.CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MILLIS)后会执行任务,创建一个 connection timed out 异常。放入 promise,main 线程和此方法用的是同一个 promise(future) 对象,main 线程 future.sync() 拿到的就是一个异常对象。
# SO_BACKLOG
属于 ServerSocketChannal 参数
- 第一次握手,client 发送 SYN 到 server,状态修改为 SYN_SEND,server 收到,将该请求放入 syn queue 队列,并状态改变为 SYN_REVD
- 第二次握手,server 回复 SYN + ACK 给 client,client 收到,状态改变为 ESTABLISHED,并发送 ACK 给 server
- 第三次握手,server 收到 ACK,将该请求从 syn queue 放入 accept queue,状态改变为 ESTABLISHED
其中
- 在 linux 2.2 之前,backlog 大小包括了两个队列的大小,在 2.2 之后,分别用下面两个参数来控制
- syn queue - 半连接队列
- 大小通过 /proc/sys/net/ipv4/tcp_max_syn_backlog 指定,在
syncookies启用的情况下,逻辑上没有最大值限制,这个设置便被忽略
- 大小通过 /proc/sys/net/ipv4/tcp_max_syn_backlog 指定,在
- accept queue - 全连接队列
- 其大小通过 /proc/sys/net/core/somaxconn 指定,在使用 listen 函数时,内核会根据传入的 backlog 参数与系统参数,取二者的较小值
- 如果 accpet queue 队列满了,server 将发送一个拒绝连接的错误信息到 client
netty 中
可以通过 option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, value) 来设置大小
源码查看默认大小
public class DefaultServerSocketChannelConfig extends DefaultChannelConfig
implements ServerSocketChannelConfig {
// 当前机器的 SOMAXCONN 值。如果无法获取该值,则将200用作 Windows 的默认值,或者将128用作其他默认值。
private volatile int backlog = NetUtil.SOMAXCONN;
// ...
}
# ulimit -n
属于操作系统参数,一个进程允许打开的文件描述符数量。临时修改有效,想要固定,可以写个脚本放到开机自启。
# TCP_NODELAY
TCP参数,立即发送数据,默认值为Ture(Netty默认为True而操作系统默认为False)。该值设置Nagle算法的启用,改算法将小的碎片数据连接成更大的报文来最小化所发送的报文的数量,如果需要发送一些较小的报文,则需要禁用该算法。Netty默认禁用该算法,从而最小化报文传输延时。
# SO_SNDBUF & SO_RCVBUF
控制滑动窗口
- SO_SNDBUF 属于 SocketChannal 参数
- SO_RCVBUF 既可用于 SocketChannal 参数,也可以用于 ServerSocketChannal 参数(建议设置到 ServerSocketChannal 上)
现在不建议更改设置,Netty 会自动设置。 [https://www.yuque.com/starries/notes/pp7fkr#4aaa5b45
](https://www.yuque.com/starries/notes/pp7fkr#4aaa5b45)
# ALLOCATOR
- 属于
SocketChannel参数 - 用来分配
ByteBuf,ctx.alloc()
配置类来决定是否使用池化,是否为直接内存。
是否使用池化
即ChannelConfig是一个接口。查看ByteBufAllocator getAllocator();方法,找到实现类 io/netty/channel/DefaultChannelConfig.java
private volatile ByteBufAllocator allocator = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT;
@Override
public ByteBufAllocator getAllocator() {
return allocator;
}
ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT为io/netty/buffer/ByteBufAllocator.java的属性。
public interface ByteBufAllocator {
ByteBufAllocator DEFAULT = ByteBufUtil.DEFAULT_ALLOCATOR;
}
相关方法
public final class ByteBufUtil {
static final ByteBufAllocator DEFAULT_ALLOCATOR;
static {
// 获取系统属性配置,可以在启动时进行配置 -Dio.netty.allocator.type=unpooled
// 如果存在 io.netty.allocator.type 这个配置,就使用指定的分配类型
// 如果没有配置,进行判断,是不是安卓,是就选用非池化类型,否则就是池化类型
String allocType = SystemPropertyUtil.get(
"io.netty.allocator.type", PlatformDependent.isAndroid() ? "unpooled" : "pooled");
allocType = allocType.toLowerCase(Locale.US).trim();
ByteBufAllocator alloc;
if ("unpooled".equals(allocType)) {
// 非池化的直接buf
alloc = UnpooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT;
logger.debug("-Dio.netty.allocator.type: {}", allocType);
} else if ("pooled".equals(allocType)) {
// 池化的直接buf
alloc = PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT;
logger.debug("-Dio.netty.allocator.type: {}", allocType);
} else {
// 池化的直接buf
alloc = PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT;
logger.debug("-Dio.netty.allocator.type: pooled (unknown: {})", allocType);
}
DEFAULT_ALLOCATOR = alloc;
THREAD_LOCAL_BUFFER_SIZE = SystemPropertyUtil.getInt("io.netty.threadLocalDirectBufferSize", 0);
MAX_CHAR_BUFFER_SIZE = SystemPropertyUtil.getInt("io.netty.maxThreadLocalCharBufferSize", 16 * 1024);
}
}
总结:
- 系统属性中配置了
io.netty.allocator.type就使用配置的分配类型,如果系统配置的不是unpooled或pooled就选用PooledByteBufAllocator - 系统属性没有配置
io.netty.allocator.type,判断是不是安卓- 安卓:
UnpooledByteBufAllocator - 其他:
PooledByteBufAllocator
- 安卓:
是否使用直接内存
找到PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT所在类
public static final PooledByteBufAllocator DEFAULT =
new PooledByteBufAllocator(PlatformDependent.directBufferPreferred());
查看_directBufferPreferred_()方法
private static final boolean DIRECT_BUFFER_PREFERRED;
// 获取系统属性 io.netty.noPreferDirect 是否不首选直接内存,取反就是首选直接内存
DIRECT_BUFFER_PREFERRED = CLEANER != NOOP
&& !SystemPropertyUtil.getBoolean("io.netty.noPreferDirect", false);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("-Dio.netty.noPreferDirect: {}", !DIRECT_BUFFER_PREFERRED);
}
public static boolean directBufferPreferred() {
return DIRECT_BUFFER_PREFERRED;
}
总结:
- 配置了系统属性
io.netty.noPreferDirectfalse首选直接内存true首选堆内存
# RCVBUF_ALLOCATOR
- 属于
SocketChannel参数 - 控制
Netty接收缓冲区大小 - 负责入站数据的分配,决定入站缓冲区的大小(并动态调整),统一采用直接内存,具体池化还是非池化由
allocator决定
与 ALLOCATOR 不同的是
- ALLOCATOR 用来配置 handler 内部的 ByteBuf
- RCVBUF_ALLOCATOR 用来配置网络 IO 时的 ByteBuf
- RCVBUF_ALLOCATOR 生成的 ByteBuf 是否为池化由 ALLOCATOR 控制
io/netty/channel/nio/AbstractNioByteChannel.java
public final void read() {
final ChannelConfig config = config();
if (shouldBreakReadReady(config)) {
clearReadPending();
return;
}
final ChannelPipeline pipeline = pipeline();
// 获取 allocator 配置,是否池化
final ByteBufAllocator allocator = config.getAllocator();
final RecvByteBufAllocator.Handle allocHandle = recvBufAllocHandle();
allocHandle.reset(config);
ByteBuf byteBuf = null;
boolean close = false;
try {
do {
// 传入 allocator 进行分配,使用 ioBuffer,自动扩缩容
byteBuf = allocHandle.allocate(allocator);
allocHandle.lastBytesRead(doReadBytes(byteBuf));
if (allocHandle.lastBytesRead() <= 0) {
// nothing was read. release the buffer.
byteBuf.release();
byteBuf = null;
close = allocHandle.lastBytesRead() < 0;
if (close) {
// There is nothing left to read as we received an EOF.
readPending = false;
}
break;
}
allocHandle.incMessagesRead(1);
readPending = false;
pipeline.fireChannelRead(byteBuf);
byteBuf = null;
} while (allocHandle.continueReading());
allocHandle.readComplete();
pipeline.fireChannelReadComplete();
if (close) {
closeOnRead(pipeline);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
handleReadException(pipeline, byteBuf, t, close, allocHandle);
} finally {
// Check if there is a readPending which was not processed yet.
// This could be for two reasons:
// * The user called Channel.read() or ChannelHandlerContext.read() in channelRead(...) method
// * The user called Channel.read() or ChannelHandlerContext.read() in channelReadComplete(...) method
//
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2254
if (!readPending && !config.isAutoRead()) {
removeReadOp();
}
}
}
allocHandle.allocate(allocator);
io/netty/channel/DefaultMaxMessagesRecvByteBufAllocator.java
@Override
public ByteBuf allocate(ByteBufAllocator alloc) {
return alloc.ioBuffer(guess());
}
io/netty/channel/AdaptiveRecvByteBufAllocator.java
static final int DEFAULT_MINIMUM = 64;
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL = 1024;
static final int DEFAULT_MAXIMUM = 65536;
/**
* 使用默认参数创建一个新的预测器。使用默认参数,预期的缓冲区大小从1024开始,不会低于64 ,也不会高于65536 。
*/
public AdaptiveRecvByteBufAllocator() {
this(DEFAULT_MINIMUM, DEFAULT_INITIAL, DEFAULT_MAXIMUM);
}
# RPC 框架
改善之前的聊天案例
# 准备工作
新增 Rpc 请求和响应消息
@Data
public abstract class Message implements Serializable {
// 省略旧的代码
public static final int RPC_MESSAGE_TYPE_REQUEST = 101;
public static final int RPC_MESSAGE_TYPE_RESPONSE = 102;
static {
// ...
messageClasses.put(RPC_MESSAGE_TYPE_REQUEST, RpcRequestMessage.class);
messageClasses.put(RPC_MESSAGE_TYPE_RESPONSE, RpcResponseMessage.class);
}
}
请求消息
@Getter
@ToString(callSuper = true)
public class RpcRequestMessage extends Message {
/**
* 调用的接口全限定名,服务端根据它找到实现
*/
private String interfaceName;
/**
* 调用接口中的方法名
*/
private String methodName;
/**
* 方法返回类型
*/
private Class<?> returnType;
/**
* 方法参数类型数组
*/
private Class[] parameterTypes;
/**
* 方法参数值数组
*/
private Object[] parameterValue;
public RpcRequestMessage(int sequenceId, String interfaceName, String methodName, Class<?> returnType, Class[] parameterTypes, Object[] parameterValue) {
super.setSequenceId(sequenceId);
this.interfaceName = interfaceName;
this.methodName = methodName;
this.returnType = returnType;
this.parameterTypes = parameterTypes;
this.parameterValue = parameterValue;
}
@Override
public int getMessageType() {
return RPC_MESSAGE_TYPE_REQUEST;
}
}
响应消息
@Data
@ToString(callSuper = true)
public class RpcResponseMessage extends Message {
/**
* 返回值
*/
private Object returnValue;
/**
* 异常值
*/
private Exception exceptionValue;
@Override
public int getMessageType() {
return RPC_MESSAGE_TYPE_RESPONSE;
}
}
服务器架子
@Slf4j
public class RpcServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
NioEventLoopGroup boss = new NioEventLoopGroup();
NioEventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup();
LoggingHandler LOGGING_HANDLER = new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG);
MessageCodecSharable MESSAGE_CODEC = new MessageCodecSharable();
// rpc 请求消息处理器,待实现
RpcRequestMessageHandler RPC_HANDLER = new RpcRequestMessageHandler();
try {
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class);
serverBootstrap.group(boss, worker);
serverBootstrap.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ProtocolFrameDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(LOGGING_HANDLER);
ch.pipeline().addLast(MESSAGE_CODEC);
ch.pipeline().addLast(RPC_HANDLER);
}
});
Channel channel = serverBootstrap.bind(8080).sync().channel();
channel.closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.error("server error", e);
} finally {
boss.shutdownGracefully();
worker.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
客户端架子
@Slf4j
public class RpcClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
NioEventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
LoggingHandler LOGGING_HANDLER = new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG);
MessageCodecSharable MESSAGE_CODEC = new MessageCodecSharable();
// rpc 响应消息处理器,待实现
RpcResponseMessageHandler RPC_HANDLER = new RpcResponseMessageHandler();
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.channel(NioSocketChannel.class);
bootstrap.group(group);
bootstrap.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ProtocolFrameDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(LOGGING_HANDLER);
ch.pipeline().addLast(MESSAGE_CODEC);
ch.pipeline().addLast(RPC_HANDLER);
}
});
Channel channel = bootstrap.connect("localhost", 8080).sync().channel();
channel.closeFuture().sync();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("client error", e);
} finally {
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
服务器端的 service 获取
public class ServicesFactory {
static Properties properties;
static Map<Class<?>, Object> map = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
static {
try (InputStream in = Config.class.getResourceAsStream("/application.properties")) {
properties = new Properties();
properties.load(in);
Set<String> names = properties.stringPropertyNames();
for (String name : names) {
if (name.endsWith("Service")) {
// 接口全限定类名
Class<?> interfaceClass = Class.forName(name);
// 接口实例全限定类名
Class<?> instanceClass = Class.forName(properties.getProperty(name));
map.put(interfaceClass, instanceClass.newInstance());
}
}
} catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException | InstantiationException | IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new ExceptionInInitializerError(e);
}
}
public static <T> T getService(Class<T> interfaceClass) {
return (T) map.get(interfaceClass);
}
}
相关配置 application.properties
serializer.algorithm=Json
com.starry.netty.server.service.HelloService=com.starry.netty.server.service.HelloServiceImpl
接口
public interface HelloService {
String hello(String name);
}
实现
public class HelloServiceImpl {
public String hello(String name) {
return name;
}
}
# 服务器 handler【静态代理】
message 包含 类名、方法名、返回类型、参数类型、具体参数。服务器可以根据这些参数反射调用方法。
@Slf4j
@ChannelHandler.Sharable
public class RpcRequestMessageHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<RpcRequestMessage> {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RpcRequestMessage message) {
RpcResponseMessage response = new RpcResponseMessage();
response.setSequenceId(message.getSequenceId());
try {
// 获取真正的实现对象
HelloService service = (HelloService)
ServicesFactory.getService(Class.forName(message.getInterfaceName()));
// 获取要调用的方法
Method method = service.getClass().getMethod(message.getMethodName(), message.getParameterTypes());
// 调用方法
Object invoke = method.invoke(service, message.getParameterValue());
// 调用成功
response.setReturnValue(invoke);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
// 调用异常
response.setExceptionValue(e);
}
// 返回结果
ctx.writeAndFlush(response);
}
}
# 客户端代码【只发消息】
@Slf4j
public class RpcClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
NioEventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
LoggingHandler LOGGING_HANDLER = new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG);
MessageCodecSharable MESSAGE_CODEC = new MessageCodecSharable();
// rpc 响应消息处理器,待实现
RpcResponseMessageHandler RPC_HANDLER = new RpcResponseMessageHandler();
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.channel(NioSocketChannel.class);
bootstrap.group(group);
bootstrap.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ProtocolFrameDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(LOGGING_HANDLER);
ch.pipeline().addLast(MESSAGE_CODEC);
ch.pipeline().addLast(RPC_HANDLER);
}
});
Channel channel = bootstrap.connect("localhost", 8080).sync().channel();
// 发送请求
channel.writeAndFlush(new RpcRequestMessage(
1,
"com.starry.netty.server.service.HelloService",
"hello",
String.class,
new Class[]{String.class},
new Object[]{"张三"}
)).addListener(future -> {
// 失败
if (!future.isSuccess()) {
Throwable cause = future.cause();
log.error("cause",cause);
}
});
channel.closeFuture().sync();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("client error", e);
} finally {
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
# 客户端 handler【只打印消息】
@Slf4j
@ChannelHandler.Sharable
public class RpcResponseMessageHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<RpcResponseMessage> {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RpcResponseMessage msg) throws Exception {
log.debug("{}", msg);
}
}
Json 序列化失败 自定义序列化、反序列类;需要 Gson 依赖
class ClassCodec implements JsonSerializer<Class<?>>, JsonDeserializer<Class<?>> {
@Override
public Class<?> deserialize(JsonElement jsonElement, Type type, JsonDeserializationContext jsonDeserializationContext) throws JsonParseException {
// 反序列化 json > object
try {
String s = jsonElement.getAsString();
return Class.forName(s);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new JsonParseException(e);
}
}
@Override
public JsonElement serialize(Class<?> aClass, Type type, JsonSerializationContext jsonSerializationContext) {
// 序列化 object > json
return new JsonPrimitive(aClass.getName());
}
}
修改代码
Json {
@Override
@SneakyThrows
public <T> T deSerialize(Class<T> clazz, byte[] bytes) {
String s = new String(bytes, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
Gson gson = new GsonBuilder().registerTypeAdapter(Class.class, new ClassCodec()).create();
return gson.fromJson(s, clazz);
}
@Override
public <T> byte[] serialize(T object) {
Gson gson = new GsonBuilder().registerTypeAdapter(Class.class, new ClassCodec()).create();
return gson.toJson(object).getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
}
}
# 客户端代码【动态代理】
包括 channel 管理,代理,接收结果
@Slf4j
public class RpcClientManager {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HelloService service = getProxyService(HelloService.class);
System.out.println(service.hello("zhangsan"));
// System.out.println(service.sayHello("lisi"));
// System.out.println(service.sayHello("wangwu"));
}
// 创建代理类
public static <T> T getProxyService(Class<T> serviceClass) {
ClassLoader loader = serviceClass.getClassLoader();
Class<?>[] interfaces = new Class[]{serviceClass};
/*
* loader – 定义代理类的类加载器
* interfaces – 代理类要实现的接口列表
* h - 将方法调用分派到的调用处理程
* */
Object o = Proxy.newProxyInstance(loader, interfaces, (proxy, method, args) -> {
// 1. 将方法调用转换为 消息对象
int sequenceId = SequenceIdGenerator.nextId();
RpcRequestMessage msg = new RpcRequestMessage(
sequenceId,
serviceClass.getName(),
method.getName(),
method.getReturnType(),
method.getParameterTypes(),
args
);
// 2. 将消息对象发送出去
getChannel().writeAndFlush(msg);
// 3. 准备一个空 Promise 对象,来接收结果 指定 promise 对象异步接收结果线程
DefaultPromise<Object> promise = new DefaultPromise<>(getChannel().eventLoop());
RpcResponseMessageHandler.PROMISES.put(sequenceId, promise);
// promise.addListener(future -> {
// // 线程
// });
// 4. 等待 promise 结果
promise.await();
if (promise.isSuccess()) {
// 调用正常
return promise.getNow();
} else {
// 调用失败
throw new RuntimeException(promise.cause());
}
});
return (T) o;
}
private static Channel channel = null;
private static final Object LOCK = new Object();
/**
* @return 获取唯一的 channel 对象 double check
*/
public static Channel getChannel() {
if (channel != null) {
return channel;
}
synchronized (LOCK) {
if (channel != null) {
return channel;
}
initChannel();
return channel;
}
}
/**
* 初始化 channel 方法
*/
private static void initChannel() {
NioEventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
LoggingHandler LOGGING_HANDLER = new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG);
MessageCodecSharable MESSAGE_CODEC = new MessageCodecSharable();
RpcResponseMessageHandler RPC_HANDLER = new RpcResponseMessageHandler();
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.channel(NioSocketChannel.class);
bootstrap.group(group);
bootstrap.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ProtocolFrameDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(LOGGING_HANDLER);
ch.pipeline().addLast(MESSAGE_CODEC);
ch.pipeline().addLast(RPC_HANDLER);
}
});
try {
channel = bootstrap.connect("localhost", 8080).sync().channel();
channel.closeFuture().addListener(future -> {
group.shutdownGracefully();
});
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("client error", e);
}
}
}
工具类,消息 id 自增
public class SequenceIdGenerator {
private static final AtomicInteger ATOMIC_INTEGER = new AtomicInteger(1);
public static Integer nextId() {
return ATOMIC_INTEGER.incrementAndGet();
}
}
# 客户端 handler【消息传递】
@Slf4j
@ChannelHandler.Sharable
public class RpcResponseMessageHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<RpcResponseMessage> {
public static final Map<Integer, Promise<Object>> PROMISES = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RpcResponseMessage msg) throws Exception {
log.debug("{}", msg);
Promise<Object> promise = PROMISES.remove(msg.getSequenceId());
if (promise != null) {
Exception exceptionValue = msg.getExceptionValue();
if(exceptionValue != null) {
promise.setFailure(exceptionValue);
} else {
Object returnValue = msg.getReturnValue();
promise.setSuccess(returnValue);
}
}
}
}
流程图 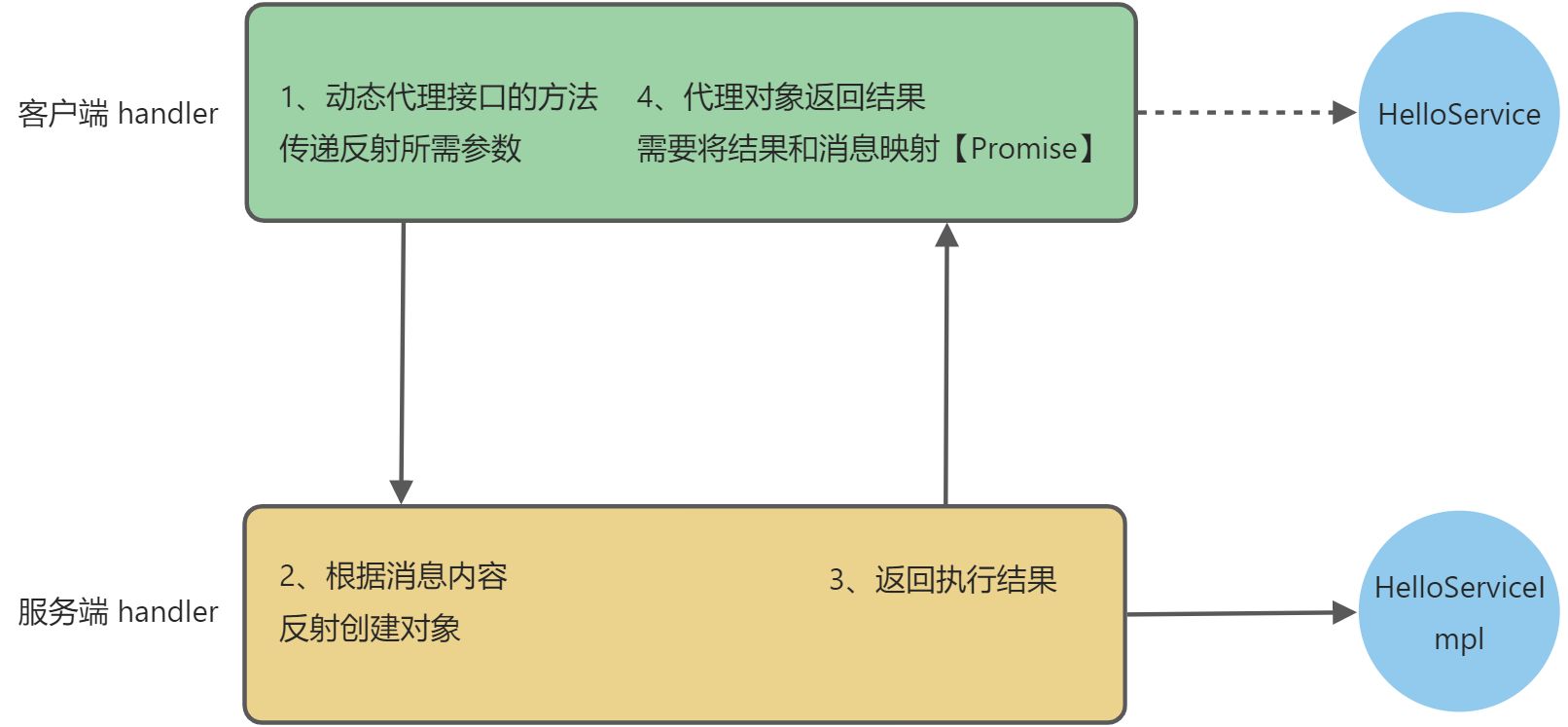
# 源码
# 启动流程
Netty 启动流程简化为如下代码:
//1 netty 中使用 NioEventLoopGroup (简称 nio boss 线程)来封装线程和 selector
Selector selector = Selector.open();
//2 创建 NioServerSocketChannel,同时会初始化它关联的 handler,以及为原生 ssc 存储 config
NioServerSocketChannel attachment = new NioServerSocketChannel();
//3 创建 NioServerSocketChannel 时,创建了 java 原生的 ServerSocketChannel
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//4 启动 nio boss 线程执行接下来的操作
//5 注册(仅关联 selector 和 NioServerSocketChannel),未关注事件
SelectionKey selectionKey = serverSocketChannel.register(selector, 0, attachment);
//6 head -> 初始化器 -> ServerBootstrapAcceptor -> tail,初始化器是一次性的,只为添加 acceptor
//7 绑定端口
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080));
//8 触发 channel active 事件,在 head 中关注 op_accept 事件
selectionKey.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
- 接收客户端连接,ServerSocketChannel
- 事件分配,Selector
- 事件处理,NioServerSocketChannel
- ServerSocketChannel向 Selector 进行注册,未关注事件,
并把 NioServerSocketChannel 作为附件添加到 ServerSocketChannel
- 指定 ServerSocketChannel 绑定的端口
- 设置要关注的事件
# bind
测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
new ServerBootstrap()
.group(new NioEventLoopGroup())
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<NioSocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(NioSocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new LoggingHandler());
}
}).bind(8080);
}
由于NioEventLoopGroup中包含了Selector,所以Selector selector = Selector.open();就暂时不关心实现。剩下的操作都是在bind中完成的。
在 bind 处进行调试
# doBind
private ChannelFuture doBind(final SocketAddress localAddress) {
// 初始化和注册(异步),返回一个 promise
final ChannelFuture regFuture = initAndRegister();
final Channel channel = regFuture.channel();
if (regFuture.cause() != null) {
return regFuture;
}
if (regFuture.isDone()) {
// ============== 初始化和注册完成
// 在这一点上,我们知道注册已经完成并成功
ChannelPromise promise = channel.newPromise();
// 绑定端口(异步执行 nio-thread)
doBind0(regFuture, channel, localAddress, promise);
return promise;
} else {
// ============== 未完成
final PendingRegistrationPromise promise = new PendingRegistrationPromise(channel);
// 添加一个监听器(异步执行 nio-thread)
regFuture.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
Throwable cause = future.cause();
if (cause != null) {
// 注册失败
promise.setFailure(cause);
} else {
// 注册成功
promise.registered();
// 绑定端口
doBind0(regFuture, channel, localAddress, promise);
}
}
});
return promise;
}
}
- 主要方法有两个
initAndRegister()和doBind0()initAndRegister()负责初始化 和 注册- 初始化可以理解为:
ServerSocketChannel.open() - 注册可以理解为:
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, 0, attachment)
- 初始化可以理解为:
doBind0()可以理解为:serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080));
- 由于
initAndRegister()是异步执行,后续获取结果时可能是执行完和没执行完- 执行完:直接进行
doBind0() - 未执行完:异步监听,进行
doBind0(),由 nio 线程执行(主线程总不能一直等着他执行完才去做其他事吧)
- 执行完:直接进行
# initAndRegister
使用反射创建一个 NioServerSocketChannel 实例 执行 init 和 register
final ChannelFuture initAndRegister() {
Channel channel = null;
try {
// channel工厂创建一个channel实例
channel = channelFactory.newChannel();
// 初始化
init(channel);
} catch (Throwable t) {
if (channel != null) {
// 抛出异常,关闭channel,设置异常信息
channel.unsafe().closeForcibly();
return new DefaultChannelPromise(channel, GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE).setFailure(t);
}
// channel 注册失败
return new DefaultChannelPromise(new FailedChannel(), GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE).setFailure(t);
}
// 注册
ChannelFuture regFuture = config().group().register(channel);
// 抛出异常
if (regFuture.cause() != null) {
if (channel.isRegistered()) {
// 已经注册,直接关闭
channel.close();
} else {
// 强制关闭
channel.unsafe().closeForcibly();
}
}
return regFuture;
}
channel = channelFactory.newChannel();调用方法在 ReflectiveChannelFactory.java
public T newChannel() {
try {
// 使用反射创建实例,返回的是 NioServerSocketChannel
return constructor.newInstance();
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw new ChannelException("Unable to create Channel from class " + constructor.getDeclaringClass(), t);
}
}
NioServerSocketChannel.java构造方法
private static final SelectorProvider DEFAULT_SELECTOR_PROVIDER = SelectorProvider.provider();
public NioServerSocketChannel() {
this(newSocket(DEFAULT_SELECTOR_PROVIDER));
}
private static ServerSocketChannel newSocket(SelectorProvider provider) {
try {
return provider.openServerSocketChannel();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new ChannelException(
"Failed to open a server socket.", e);
}
}
相当于 NIO 原生的open()方法。java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel
public static ServerSocketChannel open() throws IOException {
return SelectorProvider.provider().openServerSocketChannel();
}
也就是说channel = channelFactory.newChannel();返回的是NioServerSocketChannel,其中创建NioServerSocketChannel时也创建了 ServerSocketChannel。
完成了ServerSocketChannel.open()
完成了initAndRegister的channel = channelFactory.newChannel();接下来执行init()方法
# init
abstract void init(Channel channel) throws Exception;抽象方法,找到实现类ServerBootstrap.java
@Override
void init(Channel channel) throws Exception {
final Map<ChannelOption<?>, Object> options = options0();
synchronized (options) {
setChannelOptions(channel, options, logger);
}
final Map<AttributeKey<?>, Object> attrs = attrs0();
synchronized (attrs) {
for (Entry<AttributeKey<?>, Object> e: attrs.entrySet()) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
AttributeKey<Object> key = (AttributeKey<Object>) e.getKey();
channel.attr(key).set(e.getValue());
}
}
ChannelPipeline p = channel.pipeline();
final EventLoopGroup currentChildGroup = childGroup;
final ChannelHandler currentChildHandler = childHandler;
final Entry<ChannelOption<?>, Object>[] currentChildOptions;
final Entry<AttributeKey<?>, Object>[] currentChildAttrs;
synchronized (childOptions) {
currentChildOptions = childOptions.entrySet().toArray(newOptionArray(0));
}
synchronized (childAttrs) {
currentChildAttrs = childAttrs.entrySet().toArray(newAttrArray(0));
}
// 向NioServerSocketChannel的pipeline添加一个初始化handler,只会被执行一次。只是添加,还未被调用
p.addLast(new ChannelInitializer<Channel>() {
@Override
public void initChannel(final Channel ch) throws Exception {
final ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
ChannelHandler handler = config.handler();
if (handler != null) {
pipeline.addLast(handler);
}
// 初始化器的职责是将 ServerBootstrapAcceptor 加入至 NioServerSocketChannel
ch.eventLoop().execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
pipeline.addLast(new ServerBootstrapAcceptor(
ch, currentChildGroup, currentChildHandler, currentChildOptions, currentChildAttrs));
}
});
}
});
}
init()主要是向NioServerSocketChannel的pipeline添加一个初始化 handler
initAndRegister的init完成了,接下来要register
# register
ChannelFuture regFuture = config().group().register(channel);
register() 来到 MultithreadEventLoopGroup.java
@Override
public ChannelFuture register(Channel channel) {
return next().register(channel);
}
又来到下一个register SingleThreadEventLoop.java
@Override
public ChannelFuture register(Channel channel) {
return register(new DefaultChannelPromise(channel, this));
}
@Override
public ChannelFuture register(final ChannelPromise promise) {
ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(promise, "promise");
promise.channel().unsafe().register(this, promise);
return promise;
}
来到AbstractChannel.java#AbstractUnsafe
@Override
public final void register(EventLoop eventLoop, final ChannelPromise promise) {
if (eventLoop == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("eventLoop");
}
if (isRegistered()) {
promise.setFailure(new IllegalStateException("registered to an event loop already"));
return;
}
if (!isCompatible(eventLoop)) {
promise.setFailure(
new IllegalStateException("incompatible event loop type: " + eventLoop.getClass().getName()));
return;
}
AbstractChannel.this.eventLoop = eventLoop;
// 判断当前线程在不在 EventLoop 线程中
if (eventLoop.inEventLoop()) {
register0(promise);
} else {
// 不在
try {
// 首次执行 execute 方法时,会启动 nio 线程,之后注册等操作在 nio 线程上执行
// 因为只有一个 NioServerSocketChannel 因此,也只会有一个 boss nio 线程
// 向 eventLoop 中添加一个任务,nio线程执行
eventLoop.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
register0(promise);
}
});
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.warn(
"Force-closing a channel whose registration task was not accepted by an event loop: {}",
AbstractChannel.this, t);
closeForcibly();
closeFuture.setClosed();
safeSetFailure(promise, t);
}
}
}
上面的register()方法就是进行线程切换,由 main 线程切换到 nioEventLoopGroup(简写 nio) 线程,由 nio 线程执行register0
# register0
private void register0(ChannelPromise promise) {
try {
if (!promise.setUncancellable() || !ensureOpen(promise)) {
return;
}
boolean firstRegistration = neverRegistered;
// 真正执行注册方法
doRegister();
neverRegistered = false;
registered = true;
// 执行 NioServerSocketChannel 初始化器的 initChannel,init时添加的handler
pipeline.invokeHandlerAddedIfNeeded();
// 给promise设置值,doBind0异步监听
safeSetSuccess(promise);
// 主动触发 pipeline 中每个 handler 的 active 事件
pipeline.fireChannelRegistered();
//仅当通道从未注册过时才触发通道活动。
//如果通道被取消注册和重新注册,这可以防止触发多个通道活动。
if (isActive()) {
if (firstRegistration) {
pipeline.fireChannelActive();
} else if (config().isAutoRead()) {
beginRead();
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
// Close the channel directly to avoid FD leak.
closeForcibly();
closeFuture.setClosed();
safeSetFailure(promise, t);
}
}
# doRegister
在 AbstractNioChannel.java
真正执行注册,未关注任何事件。相当于SelectionKey selectionKey = serverSocketChannel.register(selector, 0, attachment);
@Override
protected void doRegister() throws Exception {
boolean selected = false;
for (;;) {
try {
/*
* javaChannel()就是ServerSocketChannel
* 即 ServerSocketChannel.register()
* 由于 selector 就在 eventLoop,通过 eventLoop().unwrappedSelector() 来获取 selector
* 0 未关注任何事件
* this 就是 nioServerSocketChannl
*/
selectionKey = javaChannel().register(eventLoop().unwrappedSelector(), 0, this);
return;
} catch (CancelledKeyException e) {
if (!selected) {
eventLoop().selectNow();
selected = true;
} else {
throw e;
}
}
}
}
pipeline.invokeHandlerAddedIfNeeded()
回到doRegister0,继续执行pipeline.invokeHandlerAddedIfNeeded(),执行pipline中的初始化handler,就是init时添加的handler(ServerBootstrapAcceptor)
final void invokeHandlerAddedIfNeeded() {
assert channel.eventLoop().inEventLoop();
if (firstRegistration) {
firstRegistration = false;
// We are now registered to the EventLoop. It's time to call the callbacks for the ChannelHandlers,
// that were added before the registration was done.
callHandlerAddedForAllHandlers();
}
}
private void callHandlerAddedForAllHandlers() {
final PendingHandlerCallback pendingHandlerCallbackHead;
synchronized (this) {
assert !registered;
// This Channel itself was registered.
registered = true;
pendingHandlerCallbackHead = this.pendingHandlerCallbackHead;
// Null out so it can be GC'ed.
this.pendingHandlerCallbackHead = null;
}
// This must happen outside of the synchronized(...) block as otherwise handlerAdded(...) may be called while
// holding the lock and so produce a deadlock if handlerAdded(...) will try to add another handler from outside
// the EventLoop.
PendingHandlerCallback task = pendingHandlerCallbackHead;
while (task != null) {
// 只会执行一次,执行完后,会进行remove在execute源码
task.execute();
task = task.next;
}
}
回到doRegister,继续执行safeSetSuccess给 doBind 方法中的 regFuture(Promise) 设置值。异步监听到有了值,就会执行doBind0()。
# doBind0
真正的绑定操作 NioServerSocketChannel.java
@Override
protected void doBind(SocketAddress localAddress) throws Exception {
// JDK >= 7
if (PlatformDependent.javaVersion() >= 7) {
// 相当于ServerSocketChannel.bind()
javaChannel().bind(localAddress, config.getBacklog());
} else {
javaChannel().socket().bind(localAddress, config.getBacklog());
}
}
执行完绑定后继续回到 AbstractChannel.java#AbstractUnsafe 向下执行 触发 pipeline 中每个 handler 的 active 方法,主要是 head 的方法
@Override
public final void bind(final SocketAddress localAddress, final ChannelPromise promise) {
assertEventLoop();
if (!promise.setUncancellable() || !ensureOpen(promise)) {
return;
}
if (Boolean.TRUE.equals(config().getOption(ChannelOption.SO_BROADCAST)) &&
localAddress instanceof InetSocketAddress &&
!((InetSocketAddress) localAddress).getAddress().isAnyLocalAddress() &&
!PlatformDependent.isWindows() && !PlatformDependent.maybeSuperUser()) {
logger.warn(
"A non-root user can't receive a broadcast packet if the socket " +
"is not bound to a wildcard address; binding to a non-wildcard " +
"address (" + localAddress + ") anyway as requested.");
}
boolean wasActive = isActive();
try {
// 上面的方法
doBind(localAddress);
} catch (Throwable t) {
safeSetFailure(promise, t);
closeIfClosed();
return;
}
// isActive channel 可用状态
if (!wasActive && isActive()) {
invokeLater(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// 触发 pipeline中每个handle的active方法
pipeline.fireChannelActive();
}
});
}
safeSetSuccess(promise);
}
当前 pipeline 的 handle 有:head =》 acceptor =》 tail
上面的pipeline.fireChannelActive();会调用所有 handler 的channelActive方法,最主要的是 head 的channelActive方法
DefaultChannelPipeline.java#HeadContext
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
// 传播 active 事件到下一个 handler
ctx.fireChannelActive();
// 触发 read (NioSocketChannel 这里 read,只是为了触发 channel 的事件注册,还未涉及数据读取)
// 注册读事件:读包括创建连接/读数据
readIfIsAutoRead();
}
# 关注事件
@Override
protected void doBeginRead() throws Exception {
// Channel.read() 或 ChannelHandlerContext.read() 被调用
final SelectionKey selectionKey = this.selectionKey;
if (!selectionKey.isValid()) {
return;
}
readPending = true;
// 所有关注事件 0,未关注任何事件
final int interestOps = selectionKey.interestOps();
// 判断有没有关注指定事件,这里是16就是accept
if ((interestOps & readInterestOp) == 0) {
// 设置关注事件,原来的关注事件基础上再加上指定事件,这里就是accep
// | 相当于 +
selectionKey.interestOps(interestOps | readInterestOp);
}
}
这里就完成了selectionKey.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
SelectionKey.java
// 1
public static final int OP_READ = 1 << 0;
// 4
public static final int OP_WRITE = 1 << 2;
// 8
public static final int OP_CONNECT = 1 << 3;
// 16
public static final int OP_ACCEPT = 1 << 4;
# 总结
- bind 开始
- 两个方法 initAndRegister、bind
- 其中 initAndRegister 包含 init 和 register
- initAndRegister 中反射创建了 NioServerSocketChannel(也创建了 ServerSocketChannel)【main】
- init 方法添加 acceptor handler【main】
- register 方法都是异步【nioEventLoopGroup 简写 nio thread】
- 将 JDK 的 ServerSocketChannel 注册到 Selector,未关注事件,附件为 NioServerSocketChannel
- 执行 init 时添加的 acceptor handler
- 设置 promise
- (监听到) promise 有值,执行 bind【nio thread】
- 端口绑定,ServerSocketChannel.bind
- 关注事件 16,OP_ACCEPT
# NioEventLoop
# 组成部分
- NioEventLoop 重要组成:selector、线程、任务队列
- NioEventLoop 既会处理 IO 事件,也会处理普通任务和定时任务
成员变量
public final class NioEventLoop extends SingleThreadEventLoop {
// selector,key装在数组中
private Selector selector;
// NIO原生selector,key装在set中
private Selector unwrappedSelector;
}
// 父类的父类
public abstract class SingleThreadEventExecutor extends AbstractScheduledEventExecutor implements OrderedEventExecutor {
// 任务队列
private final Queue<Runnable> taskQueue;
// 处理任务的线程
private volatile Thread thread;
// 和上面的thread差不多
private final Executor executor;
}
// 父类的父类的父类
public abstract class AbstractScheduledEventExecutor extends AbstractEventExecutor {
// 定时任务队列
PriorityQueue<ScheduledFutureTask<?>> scheduledTaskQueue;
}
# selector 何时创建
构造方法时就被创建了
NioEventLoop(NioEventLoopGroup parent, Executor executor, SelectorProvider selectorProvider,
SelectStrategy strategy, RejectedExecutionHandler rejectedExecutionHandler,
EventLoopTaskQueueFactory queueFactory) {
super(parent, executor, false, newTaskQueue(queueFactory), newTaskQueue(queueFactory),
rejectedExecutionHandler);
if (selectorProvider == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("selectorProvider");
}
if (strategy == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("selectStrategy");
}
provider = selectorProvider;
// 调用下面的方法
final SelectorTuple selectorTuple = openSelector();
selector = selectorTuple.selector;
unwrappedSelector = selectorTuple.unwrappedSelector;
selectStrategy = strategy;
}
// JDK自带NIO的Selector.open()也是用的这个provider,系统默认
private final SelectorProvider provider;
private SelectorTuple openSelector() {
final Selector unwrappedSelector;
try {
unwrappedSelector = provider.openSelector();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new ChannelException("failed to open a new selector", e);
}
// ...
}
java/nio/channels/Selector.java
/**
* 打开选择器。
* 新选择器是通过调用系统范围默认SelectorProvider对象的openSelector方法创建的。
*/
public static Selector open() throws IOException {
return SelectorProvider.provider().openSelector();
}
# 为什么两个selector
- 一个NIO原生selector
- 一个Netty修改的selector,将装载selectedKeys的set改为数组
为了遍历selectedKeys时提高性能
给selector成员变量赋值
- 传入一个参数:unwrappedSelector和selector都一样(都是原生未优化的)
- 传入两个个参数:分别赋值
private static final class SelectorTuple {
final Selector unwrappedSelector;
final Selector selector;
SelectorTuple(Selector unwrappedSelector) {
this.unwrappedSelector = unwrappedSelector;
this.selector = unwrappedSelector;
}
SelectorTuple(Selector unwrappedSelector, Selector selector) {
this.unwrappedSelector = unwrappedSelector;
this.selector = selector;
}
}
private SelectedSelectionKeySet selectedKeys;
private SelectorTuple openSelector() {
final Selector unwrappedSelector;
try {
// 原selector
unwrappedSelector = provider.openSelector();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new ChannelException("failed to open a new selector", e);
}
// 禁用key优化,默认false
if (DISABLE_KEY_SET_OPTIMIZATION) {
return new SelectorTuple(unwrappedSelector);
}
// ...
// 内部数组结构实现的set接口
final SelectedSelectionKeySet selectedKeySet = new SelectedSelectionKeySet();
Object maybeException = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Object>() {
@Override
public Object run() {
try {
// 反射获取原selector的属性
Field selectedKeysField = selectorImplClass.getDeclaredField("selectedKeys");
Field publicSelectedKeysField = selectorImplClass.getDeclaredField("publicSelectedKeys");
// jdk9+额外限制...
if (PlatformDependent.javaVersion() >= 9 && PlatformDependent.hasUnsafe()) {
// Let us try to use sun.misc.Unsafe to replace the SelectionKeySet.
// This allows us to also do this in Java9+ without any extra flags.
//...
}
// 暴力反射,允许访问
Throwable cause = ReflectionUtil.trySetAccessible(selectedKeysField, true);
if (cause != null) {
return cause;
}
cause = ReflectionUtil.trySetAccessible(publicSelectedKeysField, true);
if (cause != null) {
return cause;
}
// 替换为基于数组的selectedKeys实现
selectedKeysField.set(unwrappedSelector, selectedKeySet);
publicSelectedKeysField.set(unwrappedSelector, selectedKeySet);
return null;
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
return e;
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
return e;
}
}
});
//...
// 优化后的key,赋值给成员变量
selectedKeys = selectedKeySet;
//...
}
# NIO 线程何时启动
- 首次调用 execute 方法时
- 通过 state 状态位控制线程只会启动一次
public void execute(Runnable task) {
if (task == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("task");
}
// 判断当前线程是不是在nio线程,false,nio线程还没启动
boolean inEventLoop = inEventLoop();
// 添加任务到任务队列
addTask(task);
if (!inEventLoop) {
// 开始任务
startThread();
if (isShutdown()) {
boolean reject = false;
try {
if (removeTask(task)) {
reject = true;
}
} catch (UnsupportedOperationException e) {
// The task queue does not support removal so the best thing we can do is to just move on and
// hope we will be able to pick-up the task before its completely terminated.
// In worst case we will log on termination.
}
if (reject) {
reject();
}
}
}
// 唤醒线程
if (!addTaskWakesUp && wakesUpForTask(task)) {
wakeup(inEventLoop);
}
}
private static final int ST_NOT_STARTED = 1;
private volatile int state = ST_NOT_STARTED;
private void startThread() {
// 首次执行,未启动,都是1
if (state == ST_NOT_STARTED) {
// 原子更新值为2,下次就不会进入这里了
if (STATE_UPDATER.compareAndSet(this, ST_NOT_STARTED, ST_STARTED)) {
boolean success = false;
try {
doStartThread();
success = true;
} finally {
if (!success) {
STATE_UPDATER.compareAndSet(this, ST_STARTED, ST_NOT_STARTED);
}
}
}
}
}
private void doStartThread() {
assert thread == null;
// executor执行任务
executor.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// 在executor中执行,所以thread是nio线程
thread = Thread.currentThread();
if (interrupted) {
thread.interrupt();
}
boolean success = false;
updateLastExecutionTime();
try {
// 死循环,不断执行任务
SingleThreadEventExecutor.this.run();
success = true;
}//...
}
});
}
// 上面的代码都在SingleThreadEventExecutor.java中执行的,父类
真正的任务处理SingleThreadEventExecutor.this.run();执行子类方法,即NioEventLoop
死循环,检查到有任务,定时任务,IO事件,就会进行处理
protected void run() {
for (;;) {
try {
try {
switch (selectStrategy.calculateStrategy(selectNowSupplier, hasTasks())) {
case SelectStrategy.CONTINUE:
continue;
case SelectStrategy.BUSY_WAIT:
case SelectStrategy.SELECT:
// 设置不被唤醒,后面会用到
select(wakenUp.getAndSet(false));
if (wakenUp.get()) {
selector.wakeup();
}
// fall through
default:
}
} catch (IOException e) {
// If we receive an IOException here its because the Selector is messed up. Let's rebuild
// the selector and retry. https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/8566
rebuildSelector0();
handleLoopException(e);
continue;
}
cancelledKeys = 0;
needsToSelectAgain = false;
final int ioRatio = this.ioRatio;
if (ioRatio == 100) {
try {
processSelectedKeys();
} finally {
// Ensure we always run tasks.
runAllTasks();
}
} else {
final long ioStartTime = System.nanoTime();
try {
processSelectedKeys();
} finally {
// Ensure we always run tasks.
final long ioTime = System.nanoTime() - ioStartTime;
runAllTasks(ioTime * (100 - ioRatio) / ioRatio);
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
handleLoopException(t);
}
// Always handle shutdown even if the loop processing threw an exception.
try {
if (isShuttingDown()) {
closeAll();
if (confirmShutdown()) {
return;
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
handleLoopException(t);
}
}
}
如果没有任务线程阻塞,来任务了,线程如何知道呢?
806 NioEventLoop.java
// NIO的selector,带超时时间,防止一直阻塞
int selectedKeys = selector.select(timeoutMillis);
# wakeup 方法
回到execute方法,如果不是首次启动,就不会开启线程,此时就需要唤醒线程
public void execute(Runnable task) {
// 判断当前线程是不是在nio线程,false,nio线程还没启动
boolean inEventLoop = inEventLoop();
// 添加任务到任务队列
addTask(task);
if (!inEventLoop) {
// 开始任务
startThread();
//...
}
// 唤醒线程
if (!addTaskWakesUp && wakesUpForTask(task)) {
wakeup(inEventLoop);
}
}
调用NioEventLoop.java的wakeup方法
protected void wakeup(boolean inEventLoop) {
/**
* !inEventLoop 只有其他线程(非NIO线程)提交的任务才会唤醒
*
* wakenUp 用于控制的布尔值确定阻塞的 Selector.select 是否应该退出其选择过程。
* 在上面的run方法中会被设置为false,这里CAS的设置为true,防止多个线程多次唤醒,浪费资源
**/
if (!inEventLoop && wakenUp.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
// 唤醒selector.select(timeoutMillis)
selector.wakeup();
}
}
# 何时进入 SELECT 分支
- 当没有任务时,才会进入
SelectStrategy._SELECT_ - 当有任务时,会调用 selectNow 方法,顺便拿到 IO 事件
可以看到run方法是一个死循环
- 死循环,空转消耗性能,应该进入
case SelectStrategy.SELECT:分支,进行阻塞 - 进入条件取决于
selectStrategy.calculateStrategy(selectNowSupplier, hasTasks())
private final IntSupplier selectNowSupplier = new IntSupplier() {
@Override
public int get() throws Exception {
return selectNow();
}
};
int selectNow() throws IOException {
try {
return selector.selectNow();
} finally {
// restore wakeup state if needed
if (wakenUp.get()) {
selector.wakeup();
}
}
}
protected void run() {
for (;;) {
//...
/**
* selectNowSupplier 判断当前有没有事件 selector.selectNow()
* hasTasks 判断队列有没有任务 !taskQueue.isEmpty();
**/
switch (selectStrategy.calculateStrategy(selectNowSupplier, hasTasks())) {
case SelectStrategy.CONTINUE:
continue;
case SelectStrategy.BUSY_WAIT:
// fall-through to SELECT since the busy-wait is not supported with NIO
case SelectStrategy.SELECT:
select(wakenUp.getAndSet(false));
//...
try {
// 处理IO事件
processSelectedKeys();
} finally {
// 处理任务
runAllTasks();
}
//...
}
}
DefaultSelectStrategy.java
public int calculateStrategy(IntSupplier selectSupplier, boolean hasTasks) throws Exception {
return hasTasks ? selectSupplier.get() : SelectStrategy.SELECT;
}
- hasTasks 为 false 时进入 select 分支
- hasTasks 为 true 时,有任务,并立即从 selector 上获取事件,即同时处理了任务和 IO 事件
# select 阻塞多久
没有定时任务的情况
- selectDeadLineNanos:截至时间 = 当前时间 + 1s
- timeoutMillis:超时时间 = 1s + 0.5ms
private void select(boolean oldWakenUp) throws IOException {
Selector selector = this.selector;
try {
int selectCnt = 0;
long currentTimeNanos = System.nanoTime();
long selectDeadLineNanos = currentTimeNanos + delayNanos(currentTimeNanos);
for (;;) {
long timeoutMillis = (selectDeadLineNanos - currentTimeNanos + 500000L) / 1000000L;
// 超时 结束死循环
if (timeoutMillis <= 0) {
if (selectCnt == 0) {
selector.selectNow();
selectCnt = 1;
}
break;
}
// 有任务 结束死循环
if (hasTasks() && wakenUp.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
selector.selectNow();
selectCnt = 1;
break;
}
int selectedKeys = selector.select(timeoutMillis);
selectCnt ++;
// 有IO事件 结束死循环
if (selectedKeys != 0 || oldWakenUp || wakenUp.get() || hasTasks() || hasScheduledTasks()) {
// - Selected something,
// - waken up by user, or
// - the task queue has a pending task.
// - a scheduled task is ready for processing
break;
}
if (Thread.interrupted()) {
// Thread was interrupted so reset selected keys and break so we not run into a busy loop.
// As this is most likely a bug in the handler of the user or it's client library we will
// also log it.
//
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2426
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Selector.select() returned prematurely because " +
"Thread.currentThread().interrupt() was called. Use " +
"NioEventLoop.shutdownGracefully() to shutdown the NioEventLoop.");
}
selectCnt = 1;
break;
}
long time = System.nanoTime();
if (time - TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.toNanos(timeoutMillis) >= currentTimeNanos) {
// timeoutMillis elapsed without anything selected.
selectCnt = 1;
} else if (SELECTOR_AUTO_REBUILD_THRESHOLD > 0 &&
selectCnt >= SELECTOR_AUTO_REBUILD_THRESHOLD) {
// The code exists in an extra method to ensure the method is not too big to inline as this
// branch is not very likely to get hit very frequently.
selector = selectRebuildSelector(selectCnt);
selectCnt = 1;
break;
}
currentTimeNanos = time;
}
if (selectCnt > MIN_PREMATURE_SELECTOR_RETURNS) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Selector.select() returned prematurely {} times in a row for Selector {}.",
selectCnt - 1, selector);
}
}
} catch (CancelledKeyException e) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug(CancelledKeyException.class.getSimpleName() + " raised by a Selector {} - JDK bug?",
selector, e);
}
// Harmless exception - log anyway
}
}
SingleThreadEventExecutor.java
private static final long SCHEDULE_PURGE_INTERVAL = TimeUnit.SECONDS.toNanos(1);
// 返回距离执行截止日期最近的计划任务的剩余时间
protected long delayNanos(long currentTimeNanos) {
ScheduledFutureTask<?> scheduledTask = peekScheduledTask();
if (scheduledTask == null) {
// 不是定时任务,返回1秒
return SCHEDULE_PURGE_INTERVAL;
}
// 是定时任务,返回下一个定时任务执行的时间
return scheduledTask.delayNanos(currentTimeNanos);
}
# select 空轮询bug
select没有被成功阻塞 默认空转次数>=512新建一个selector,替换旧的
NioEventLoop.java
private static final int SELECTOR_AUTO_REBUILD_THRESHOLD;
static {
// 从读取系统配置,默认512
int selectorAutoRebuildThreshold = SystemPropertyUtil.getInt("io.netty.selectorAutoRebuildThreshold", 512);
if (selectorAutoRebuildThreshold < MIN_PREMATURE_SELECTOR_RETURNS) {
selectorAutoRebuildThreshold = 0;
}
SELECTOR_AUTO_REBUILD_THRESHOLD = selectorAutoRebuildThreshold;
}
private void select(boolean oldWakenUp) throws IOException {
Selector selector = this.selector;
try {
// select 次数
int selectCnt = 0;
long currentTimeNanos = System.nanoTime();
long selectDeadLineNanos = currentTimeNanos + delayNanos(currentTimeNanos);
for (;;) {
long timeoutMillis = (selectDeadLineNanos - currentTimeNanos + 500000L) / 1000000L;
// 超时 结束死循环
if (timeoutMillis <= 0) {
if (selectCnt == 0) {
selector.selectNow();
selectCnt = 1;
}
break;
}
// 有任务 结束死循环
if (hasTasks() && wakenUp.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
selector.selectNow();
selectCnt = 1;
break;
}
int selectedKeys = selector.select(timeoutMillis);
// 每循环一次,次数增加
selectCnt ++;
// 有IO事件 结束死循环
if (selectedKeys != 0 || oldWakenUp || wakenUp.get() || hasTasks() || hasScheduledTasks()) {
// - Selected something,
// - waken up by user, or
// - the task queue has a pending task.
// - a scheduled task is ready for processing
break;
}
if (Thread.interrupted()) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Selector.select() returned prematurely because " +
"Thread.currentThread().interrupt() was called. Use " +
"NioEventLoop.shutdownGracefully() to shutdown the NioEventLoop.");
}
selectCnt = 1;
break;
}
long time = System.nanoTime();
if (time - TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.toNanos(timeoutMillis) >= currentTimeNanos) {
// 超时,计数重置
selectCnt = 1;
} else if (SELECTOR_AUTO_REBUILD_THRESHOLD > 0 &&
selectCnt >= SELECTOR_AUTO_REBUILD_THRESHOLD) {
// 如果空转次数>=阈值,新建一个selector,替换旧的selector
selector = selectRebuildSelector(selectCnt);
selectCnt = 1;
break;
}
currentTimeNanos = time;
}
if (selectCnt > MIN_PREMATURE_SELECTOR_RETURNS) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Selector.select() returned prematurely {} times in a row for Selector {}.",
selectCnt - 1, selector);
}
}
} catch (CancelledKeyException e) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug(CancelledKeyException.class.getSimpleName() + " raised by a Selector {} - JDK bug?",
selector, e);
}
// Harmless exception - log anyway
}
}
# ioRatio
ioRatio控制什么,设置100有什么用? NioEventLoop可以处理IO事件和其他任务。不同的操作所耗费的时间是不同的,想要控制NioEventLoop处理IO事件花费时间占执行所有操作的总时间的比例,需要通过ioRatio来控制,默认各占用50
private volatile int ioRatio = 50;
protected void run() {
//...
final int ioRatio = this.ioRatio;
if (ioRatio == 100) {
try {
processSelectedKeys();
} finally {
// 100比例,确认任务也能执行,不设超时时间
// 如果处理耗时任务,会长时间阻塞
runAllTasks();
}
} else {
final long ioStartTime = System.nanoTime();
try {
processSelectedKeys();
} finally {
// 处理IO占用的时间
final long ioTime = System.nanoTime() - ioStartTime;
// ioTime * (100-50)/50 = ioTime * 1 = ioTime
// 即运行任务时间和处理io时间一样,如果没处理完,下次循环再继续
runAllTasks(ioTime * (100 - ioRatio) / ioRatio);
}
}
//...
}
# 处理事件
NioEventLoop.java
private void processSelectedKeys() {
// 优化后的key集合不为null
if (selectedKeys != null) {
processSelectedKeysOptimized();
} else {
processSelectedKeysPlain(selector.selectedKeys());
}
}
private void processSelectedKeysOptimized() {
for (int i = 0; i < selectedKeys.size; ++i) {
final SelectionKey k = selectedKeys.keys[i];
// null out entry in the array to allow to have it GC'ed once the Channel close
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2363
selectedKeys.keys[i] = null;
// 获取附件,nioServerSocketChannel
// https://www.yuque.com/starries/notes/wyq9en#af0XE
final Object a = k.attachment();
if (a instanceof AbstractNioChannel) {
// 处理事件
processSelectedKey(k, (AbstractNioChannel) a);
} else {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
NioTask<SelectableChannel> task = (NioTask<SelectableChannel>) a;
processSelectedKey(k, task);
}
if (needsToSelectAgain) {
// null out entries in the array to allow to have it GC'ed once the Channel close
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2363
selectedKeys.reset(i + 1);
selectAgain();
i = -1;
}
}
}
private void processSelectedKey(SelectionKey k, AbstractNioChannel ch) {
final AbstractNioChannel.NioUnsafe unsafe = ch.unsafe();
if (!k.isValid()) {
final EventLoop eventLoop;
try {
eventLoop = ch.eventLoop();
} catch (Throwable ignored) {
return;
}
if (eventLoop != this || eventLoop == null) {
return;
}
unsafe.close(unsafe.voidPromise());
return;
}
try {
int readyOps = k.readyOps();
// 连接事件,服务器没啥用,客户端用
if ((readyOps & SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT) != 0) {
int ops = k.interestOps();
ops &= ~SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT;
k.interestOps(ops);
unsafe.finishConnect();
}
// 可写事件
if ((readyOps & SelectionKey.OP_WRITE) != 0) {
ch.unsafe().forceFlush();
}
// 可读/可连接事件
if ((readyOps & (SelectionKey.OP_READ | SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT)) != 0 || readyOps == 0) {
unsafe.read();
}
} catch (CancelledKeyException ignored) {
unsafe.close(unsafe.voidPromise());
}
}
# Accept 流程
NIO中Accept主要流程:
- selector.select()阻塞线程,直到事件发生
- 遍历selectionKeys
- 获取一个key,判断事件类型是否为Accept
- 创建SocketChannel,设置为非阻塞
- 将SocketChannel注册到selector中
- 关注selectionKeys的read事件
前面3步在NioEventLoop中都分析了,下面主要分析后3步
// 可读事件 1
// 可连接事件 16
if ((readyOps & (SelectionKey.OP_READ | SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT)) != 0 || readyOps == 0) {
unsafe.read();
}
AbstractNioMessageChannel.java#NioMessageUnsafe
private final class NioMessageUnsafe extends AbstractNioUnsafe {
private final List<Object> readBuf = new ArrayList<Object>();
@Override
public void read() {
assert eventLoop().inEventLoop();
final ChannelConfig config = config();
final ChannelPipeline pipeline = pipeline();
final RecvByteBufAllocator.Handle allocHandle = unsafe().recvBufAllocHandle();
allocHandle.reset(config);
boolean closed = false;
Throwable exception = null;
try {
try {
do {
// ssc.accept得到sc
// 创建nioSocketChannel,放入上面的list,readBuf
// 封装为一个消息对象,使用pipeline进行处理
int localRead = doReadMessages(readBuf);
if (localRead == 0) {
break;
}
if (localRead < 0) {
closed = true;
break;
}
allocHandle.incMessagesRead(localRead);
} while (allocHandle.continueReading());
} catch (Throwable t) {
exception = t;
}
int size = readBuf.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i ++) {
readPending = false;
// nioServerSocketChannel的pipeline对消息进行处理
// head -> accpetor -> tail 主要是acceptor
// https://www.yuque.com/starries/notes/wyq9en#WYMOj
pipeline.fireChannelRead(readBuf.get(i));
}
readBuf.clear();
allocHandle.readComplete();
pipeline.fireChannelReadComplete();
if (exception != null) {
closed = closeOnReadError(exception);
pipeline.fireExceptionCaught(exception);
}
if (closed) {
inputShutdown = true;
if (isOpen()) {
close(voidPromise());
}
}
} finally {
if (!readPending && !config.isAutoRead()) {
removeReadOp();
}
}
}
}
NioServerSocketChannel.java
protected int doReadMessages(List<Object> buf) throws Exception {
// serverSocketChannel.accept(),返回SocketChannel
SocketChannel ch = SocketUtils.accept(javaChannel());
try {
if (ch != null) {
// 创建一个NioSocketChannel传入nioServerSocketChannel和socketChannel,添加到要处理的list中
buf.add(new NioSocketChannel(this, ch));
return 1;
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.warn("Failed to create a new channel from an accepted socket.", t);
try {
ch.close();
} catch (Throwable t2) {
logger.warn("Failed to close a socket.", t2);
}
}
return 0;
}
SocketUtils.java
public static SocketChannel accept(final ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel) throws IOException {
try {
return AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedExceptionAction<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
public SocketChannel run() throws IOException {
return serverSocketChannel.accept();
}
});
} catch (PrivilegedActionException e) {
throw (IOException) e.getCause();
}
}
ServerBootstrap.java#ServerBootstrapAcceptor acceptor对消息进行处理
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) {
// nioSocketChannel
final Channel child = (Channel) msg;
child.pipeline().addLast(childHandler);
setChannelOptions(child, childOptions, logger);
for (Entry<AttributeKey<?>, Object> e: childAttrs) {
child.attr((AttributeKey<Object>) e.getKey()).set(e.getValue());
}
try {
// 从NioEventLoopGroup中另外选择一个nioEventLoop(非boss线程)的selector用来监听上面channel的事件
// 注册到selector上
childGroup.register(child).addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
if (!future.isSuccess()) {
forceClose(child, future.cause());
}
}
});
} catch (Throwable t) {
forceClose(child, t);
}
}
和之前启动时的注册类似 AbstractChannel.java
public final void register(EventLoop eventLoop, final ChannelPromise promise) {
if (eventLoop == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("eventLoop");
}
if (isRegistered()) {
promise.setFailure(new IllegalStateException("registered to an event loop already"));
return;
}
if (!isCompatible(eventLoop)) {
promise.setFailure(
new IllegalStateException("incompatible event loop type: " + eventLoop.getClass().getName()));
return;
}
AbstractChannel.this.eventLoop = eventLoop;
// 判断是不是在同一个线程,不是
// 一个是boss,一个是worker
if (eventLoop.inEventLoop()) {
register0(promise);
} else {
try {
// 线程切换到worker
eventLoop.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
register0(promise);
}
});
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.warn(
"Force-closing a channel whose registration task was not accepted by an event loop: {}",
AbstractChannel.this, t);
closeForcibly();
closeFuture.setClosed();
safeSetFailure(promise, t);
}
}
}
private void register0(ChannelPromise promise) {
try {
if (!promise.setUncancellable() || !ensureOpen(promise)) {
return;
}
boolean firstRegistration = neverRegistered;
// SocketChannel注册到worker的selector上
doRegister();
neverRegistered = false;
registered = true;
// 触发nioSocketChannel上的初始化事件
// 即添加一个LoggingHandler
/*
new ServerBootstrap()
.group(new NioEventLoopGroup())
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<NioSocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(NioSocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new LoggingHandler());
}
}).bind(8080);
*/
// 触发前 head -> new ChannelInitializer() -> tail
pipeline.invokeHandlerAddedIfNeeded();
// 触发后 head -> LoggingHandler -> tail
safeSetSuccess(promise);
pipeline.fireChannelRegistered();
if (isActive()) {
if (firstRegistration) {
// 触发pipeline上的active事件,关注read事件
pipeline.fireChannelActive();
} else if (config().isAutoRead()) {
beginRead();
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
closeForcibly();
closeFuture.setClosed();
safeSetFailure(promise, t);
}
}
AbstractNioChannel.java
protected void doRegister() throws Exception {
boolean selected = false;
for (;;) {
try {
// javaChannel():SocketChannel
// eventLoop().unwrappedSelector():worker的selector
// this:nioSocketChannel附件
selectionKey = javaChannel().register(eventLoop().unwrappedSelector(), 0, this);
return;
} catch (CancelledKeyException e) {
if (!selected) {
// Force the Selector to select now as the "canceled" SelectionKey may still be
// cached and not removed because no Select.select(..) operation was called yet.
eventLoop().selectNow();
selected = true;
} else {
// We forced a select operation on the selector before but the SelectionKey is still cached
// for whatever reason. JDK bug ?
throw e;
}
}
}
}
和之前启动时关注事件类似 AbstractNioChannel.java
protected void doBeginRead() throws Exception {
// Channel.read() or ChannelHandlerContext.read() was called
final SelectionKey selectionKey = this.selectionKey;
if (!selectionKey.isValid()) {
return;
}
readPending = true;
final int interestOps = selectionKey.interestOps();
if ((interestOps & readInterestOp) == 0) {
// 关注read事件
selectionKey.interestOps(interestOps | readInterestOp);
}
}
#
# Read 流程
accept和read共用一个入口
// 此时ops为1
if ((readyOps & (SelectionKey.OP_READ | SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT)) != 0 || readyOps == 0) {
unsafe.read();
}
进入AbstractNioByteChannel.java#NioByteUnsafe
public final void read() {
final ChannelConfig config = config();
if (shouldBreakReadReady(config)) {
clearReadPending();
return;
}
final ChannelPipeline pipeline = pipeline();
// https://www.yuque.com/starries/notes/wyq9en#dYHse
// 根据配置创建ByteBufAllocator(池化非池化、直接非直接内存)
final ByteBufAllocator allocator = config.getAllocator();
// 可以动态调整byteBuf的大小,强制使用直接ioBuffer,即直接内存
final RecvByteBufAllocator.Handle allocHandle = recvBufAllocHandle();
allocHandle.reset(config);
ByteBuf byteBuf = null;
boolean close = false;
try {
do {
// 根据配置创建byteBuf
byteBuf = allocHandle.allocate(allocator);
// 读取客户端发送的数据,填充至byteBuf
allocHandle.lastBytesRead(doReadBytes(byteBuf));
if (allocHandle.lastBytesRead() <= 0) {
// nothing was read. release the buffer.
byteBuf.release();
byteBuf = null;
close = allocHandle.lastBytesRead() < 0;
if (close) {
// There is nothing left to read as we received an EOF.
readPending = false;
}
break;
}
allocHandle.incMessagesRead(1);
readPending = false;
// 触发read事件,让pipeline上的handler进行处理
// childHandler 即 tail -> logging -> tail
pipeline.fireChannelRead(byteBuf);
byteBuf = null;
} while (allocHandle.continueReading());
allocHandle.readComplete();
// 触发 read complete事件
pipeline.fireChannelReadComplete();
if (close) {
closeOnRead(pipeline);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
handleReadException(pipeline, byteBuf, t, close, allocHandle);
} finally {
// Check if there is a readPending which was not processed yet.
// This could be for two reasons:
// * The user called Channel.read() or ChannelHandlerContext.read() in channelRead(...) method
// * The user called Channel.read() or ChannelHandlerContext.read() in channelReadComplete(...) method
//
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2254
if (!readPending && !config.isAutoRead()) {
removeReadOp();
}
}
}

